Introduction
In the era of explosive internet growth, cybersecurity threats are more prevalent than ever. Thus, tools that protect personal data have become essential. One of the most common and accessible tools is the proxy. So, what is a proxy? Can a proxy truly secure your information and optimize your internet experience? Let’s dive into the details below.
What is a Proxy?
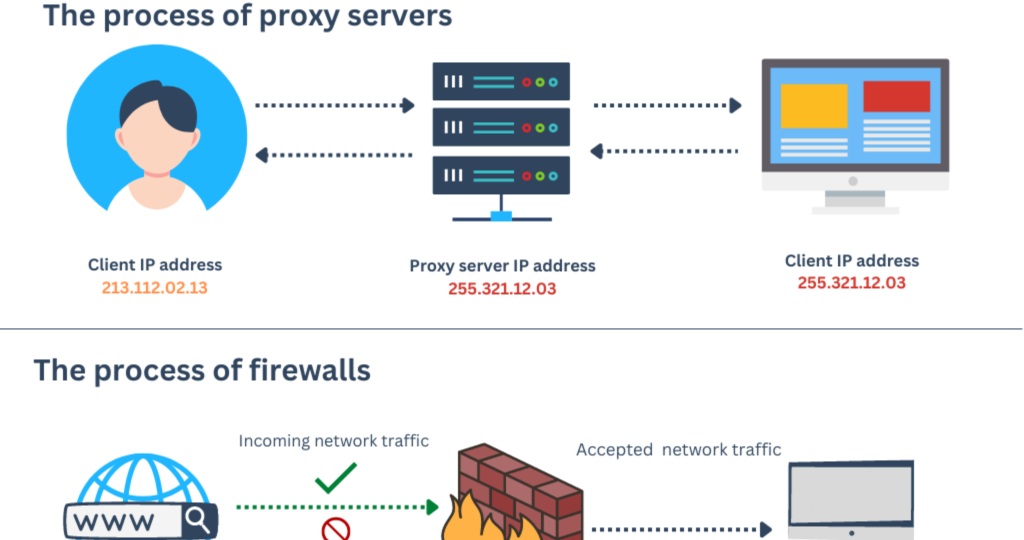
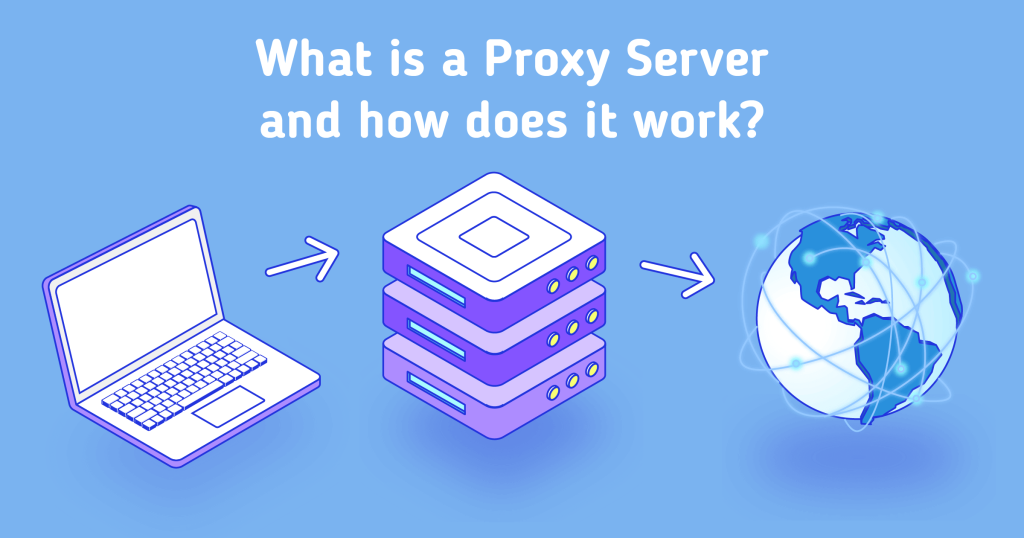
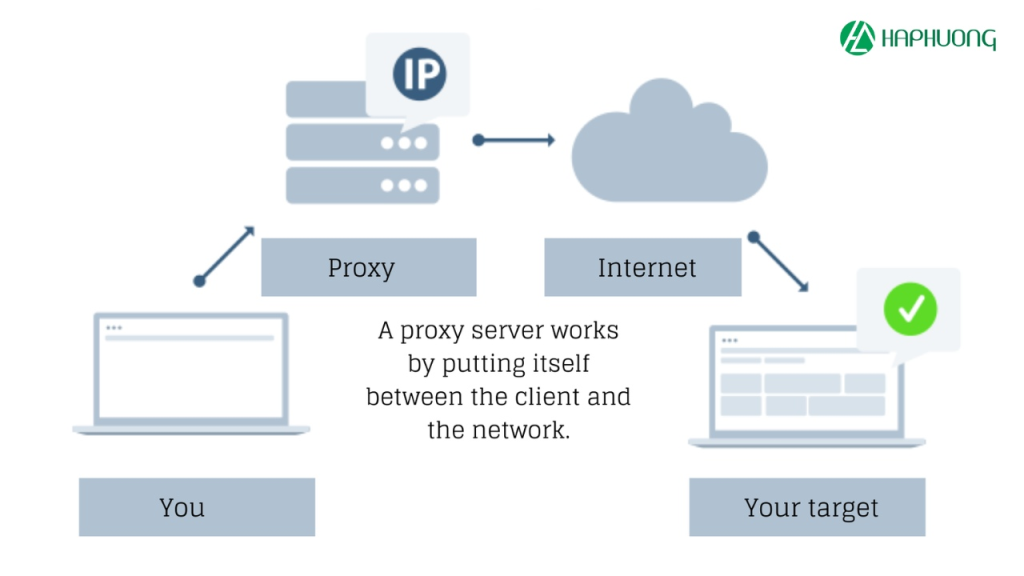
A proxy, or proxy server, is an intermediary server between your device (computer, smartphone) and the internet. When you request to access a website, instead of your device connecting directly to the destination server, the request is routed through a proxy server.
In simple terms, what is a proxy? A proxy acts as a “middleman” that interacts with the internet on your behalf. It receives your request, forwards it to the destination server, retrieves the response, and sends it back to you.
A proxy helps hide your real IP address, enhances security, filters content, manages access, and optimizes bandwidth usage.

How Does a Proxy Work?
To fully understand what a proxy is, it’s crucial to grasp its basic working principles:
- The user sends a request to access a website (e.g., www.example.com).
- The proxy server receives the request and modifies or hides the user’s original information (IP address).
- The proxy server forwards the request to the destination website server.
- The destination server sends the response back to the proxy.
- The proxy checks, filters (if needed), and delivers the content to the user.
1. HTTP Proxy
An HTTP proxy works specifically with HTTP or HTTPS websites. It is commonly used for basic web browsing. When a user accesses a website, the HTTP proxy forwards the request and response between the user and the web server, acting as an intermediary. It’s the most basic and straightforward proxy for navigating standard websites.
- Use Case: Ideal for general browsing and accessing websites using HTTP and HTTPS protocols.
2. SOCKS Proxy
A SOCKS proxy is more versatile than an HTTP proxy, supporting a wider range of data types, such as email, torrents, and online gaming. It does not require data to be in the HTTP or HTTPS format, making it suitable for more complex data transmission. SOCKS proxies are used when you need to handle various types of traffic other than just web browsing.
- Use Case: Great for activities like torrenting, online gaming, or handling email, where an HTTP proxy might not suffice.
3. Transparent Proxy
A transparent proxy does not hide the user’s IP address. These proxies are often used within organizations to monitor or filter content. While transparent proxies don’t provide full anonymity, they can provide HTTP traffic filtering to ensure compliance with internal policies or external regulations.
- Use Case: Commonly used in organizations to filter or block access to certain websites without fully concealing the user’s identity.
4. Anonymous Proxy
An anonymous proxy hides the user’s IP address, but it reveals that a proxy server is being used. While it helps enhance privacy, it is not completely foolproof. Websites can still detect that the user is connected via a proxy, which may not be ideal for users seeking complete anonymity.
- Use Case: Suitable for users who want basic privacy protection when browsing the web but do not require total anonymity.
5. Elite Proxy
An elite proxy offers the highest level of anonymity by completely hiding the user’s IP address and concealing the fact that a proxy is being used. This type of proxy is ideal for users who need to maintain complete privacy while browsing the internet.
Use Case: Best suited for users who require the highest level of anonymity, such as journalists, activists, or individuals in countries with restricted internet access.
T1. Hiding Real IP Address
A proxy server hides your real IP address, protecting your location and identity online. By acting as an intermediary between your device and the internet, a proxy server ensures that your IP address remains concealed, making it harder for malicious entities to track or attack you.
2. Protection from Direct Attacks
Since proxy servers act as intermediaries, they significantly reduce the chance of direct cyber-attacks on your device. Any cyber-attacks or hacking attempts target the proxy server rather than your actual system, ensuring your device remains shielded from direct threats.
3. Filtering Harmful Content
Proxy servers can block unsafe websites, preventing malware, viruses, and harmful content from reaching your system. By filtering out known malicious sites, proxy servers help prevent cyber-attacks, ransomware, or phishing attempts, adding a layer of security to your online activity.
4. Speeding Up Access
Proxy servers can cache frequently visited data, boosting website loading times. This reduces the time it takes to load pages, improving browsing efficiency. Cached content allows proxy servers to serve data quickly, offering faster access to commonly visited websites without constantly pulling data from the origin server.
5. Managing Internet Access
Organizations use proxy servers to control the websites employees can access, improving productivity and ensuring compliance with company policies. By restricting access to non-work-related or harmful sites, proxy servers help manage bandwidth usage and maintain a secure, focused network environment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using a Proxy
Advantages
- Browse the internet anonymously.
- Access geo-restricted content easily.
- Speed up web browsing through cached data.
- Reduce the risk of direct cyberattacks.
Disadvantages
- Free proxies may pose security risks and data leaks.
- Poor-quality proxies can slow down internet speed.
- Some websites may block access from known proxies.
When Should You Use a Proxy?
- When you need to enhance personal data security.
- When accessing websites blocked by your ISP or government.
- When you want to save bandwidth and improve browsing speed.
- When you need to access content restricted to specific geographic regions.
Proxy vs. VPN: What’s the Difference?
Although proxies and VPNs both hide IP addresses, they differ significantly:
| Criteria | Proxy | VPN |
|---|---|---|
| IP Address Masking | Yes | Yes |
| Data Encryption | No | Yes |
| Speed | Faster | Slower (due to encryption) |
| Security | Moderate | High |
| Use Case | Basic web browsing | Full connection security |
Internal Link Suggestions:
- Read more: Proxy vs VPN
External Link Reference:
Wikipedia – Proxy Server
